Secure websites: TLS encryption becomes mandatory
GDPR-compliant requirements for data transmission
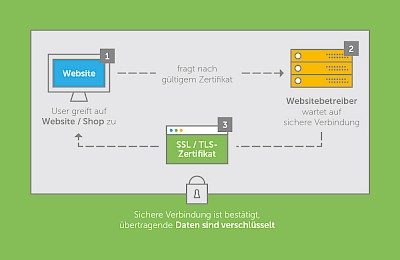
The new General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is just around the corner and this means a TLS encryption obligation for all company websites. After all, anyone who fails to secure their personal data is acting in breach of the regulations and may face warnings or fines. For the user, TLS encryption is an important indicator of whether a website is secure. TLS, short for Transport Layer Security, is the encryption of data between the user and the website operator. The term SSL is also often used, whereby SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer and is the predecessor of TLS. However, both have the same purpose - to encrypt personal data.
How does the encryption work?
Encryption is carried out using a public key procedure. Data is encoded by the sender and decoded again by the recipient. When a user accesses the website, a certificate is sent back to them. The user's browser can thus check the identity of the server and ensure encrypted content. The verification of the visited website is carried out by a so-called chain of trust between the user's browser and the server of the visited website.
How do you recognize encryption?
You can recognize successful encryption by a green address bar or a lock next to the URL. This allows the user to see that the respective website operator has a valid certificate and that the data is therefore protected against access and manipulation by third parties. The abbreviation HTTPS also indicates encryption. It means that the use of HTTP runs via SSL or TLS encryption. If a website is not encrypted, it is shown with a circled "i" or as "not secure".
What are the advantages of TLS encryption?
The primary advantage for users, but also for website operators, is the encryption of data. This results in increased user trust. Through this confidentiality, the website operator guarantees the user that, for example, credit card data or passwords cannot be read by third parties. TLS certificates also play an important role in SEO. Website operators can benefit from certificates with search engines. This is because Google, Bing and the like take encryption into account and give certified website operators a better ranking in search results.
Why is encryption mandatory?
According to the new General Data Protection Regulation, which came into force on May 25, 2018, all personal data must be encrypted in accordance with the "state of the art". To ensure this, the use of TLS encryption is mandatory. Most website operators have contact forms or the option to order newsletters. In both cases, personal data is collected. By law, this data must be transmitted securely and protected from third parties. The Bavarian State Office for Data Protection Supervision (BayLDA) has already checked the security level of more than 2000 Bavarian companies. Many companies did not meet the data protection requirements and were therefore admonished by the BayLDA.
What types of certificates are there?
There are various certificates. Depending on what kind of website you operate, you have three different options to choose from. With all three certificates, the data transmitted between the user's browser and the web server is encrypted.
1. domain-validated (DV)
The DV certificate is the certification with the lowest requirements. Only the e-mail address is authenticated, but no identity is checked. Information is only displayed via the domain. The word "Secure" appears next to the URL together with a green lock.
2. organization validation (OV)
The OV certification does not differ from the DV certification in the browser bar display. However, if the user provides more information about the certificate by clicking on the green address bar, information about the owner of the domain is displayed. The identity of the owner is checked here.
3. extended validation (EV)
EV encryption has the strongest authentication of all three certificates. Here the user can see that it is the EV certificate. The URL line in the browser is highlighted in green. In addition, the company name is displayed and the user can be sure that it is a legal and registered company.
Conclusion
We recommend that you take care of the encrypted transmission of your website as soon as possible in order to protect your users' personal data and avoid possible fines. If you would like to find out more about the options and the correct use of certificates, please contact us at any time.

TSL encryption: Who is familiar with it?
Do you have further questions about TSL encryption, would you like to make your website more secure and need professional help? We will be happy to support you. Simply contact us without obligation!