Conversion rate
Online marketing is all about conversions. The English term literally means "conversion" and usually describes the conversion of interested parties into customers in the online marketing context. The conversion rate can be used to calculate the ratio at which potential customers carry out a desired action on a website. Website operators and companies can decide for themselves which type of conversion is of interest to them.
In this blog article, we explain what types of conversions there are, what the conversion rate is and how to calculate it. Finally, you will learn what role the user behavior of prospective customers and the user-friendliness of websites plays and how an increase in the conversion rate can be achieved with various ways to improve it.
Metrics in online marketing: What is the conversion rate?
The conversion rate - also known as the conversion rate - is the percentage of page visits or visitors who complete a specific transaction on a website. The percentage therefore indicates how many of the defined target persons or interested parties bring the company closer to its goal. The exact action to be analyzed can be defined individually for each landing page of a website, for example. It is common for websites to pursue several conversion goals and several percentages can be determined accordingly.
Conversion rate: What types of conversions are there?
Not all conversions are the same. Depending on where the prospective customer or customer is in the purchase funnel and what goal you are pursuing with advertising campaigns, landing pages etc., it can mean any desired transaction from clicking a button to making contact or making a purchase. Do you want to draw attention to a specific product with advertisements? Then you want potential prospects to click on your ads and convert into an active lead. If, on the other hand, you want to encourage visitors to sign up for a newsletter or to fill out a form, the submission of the data collected for this purpose is a conversion. Other possible conversions can therefore be
- Download of e-books
- Newsletter registration
- making contact
- Clicking on advertisements
- Product purchase
- Product registration
- Reviews and ratings
Measurement of micro-conversions
Tracking micro-conversions can be helpful for improving the design and structure of landing pages. This includes, for example, the actual duration for which an embedded video is viewed, scrolling or scrolling over certain areas or clicking on links. These are subtleties, but they have a major impact on achieving a higher-level conversion.
How do you calculate the conversion rate?
To calculate the conversion rate, you must first determine whether the number of users or the number of page visits or page views should be used for comparison. This is because a user can visit your site several times and still only convert once.
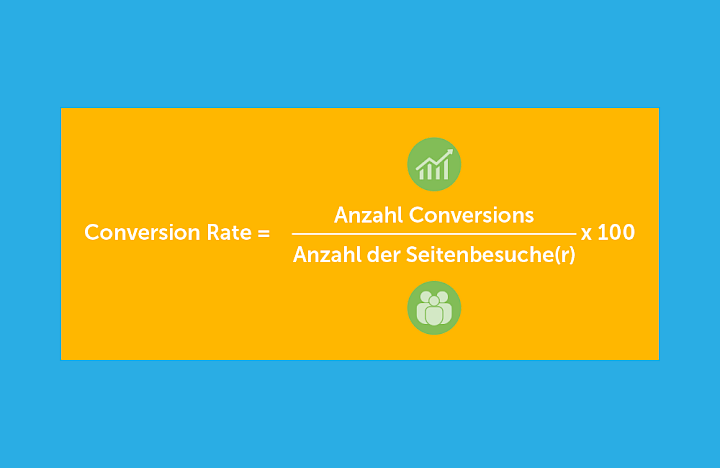
The conversion rate is therefore calculated either from the number of conversions and the number of page visits or from the execution of the desired transaction and the number of page visits. The formula for calculating the metric is as follows:Conversion rate = (number of conversions x 100) / (number of page visitors or page views)
Measuring & tracking conversions: What are the benefits of calculating the conversion rate?
The conversion rate is one of the most important KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that can be used to measure and assess the performance of advertising measures or a website. KPIs therefore form the basis for monitoring success and optimization in online marketing and other business areas. Basically, the higher the percentage, the more effectively a company achieves its goal. This is because a high conversion rate means that a large percentage of your website visitors perform actions that are relevant to you, such as registering, making contact or making a purchase. If the metric is low, however, this may indicate problems. Your offer is not interesting for the market, your advertising measures are not appealing or your website is not user-friendly. In addition, a high conversion rate can also improve your search engine ranking. Search engines such as Google reward websites that offer a positive user experience with a better ranking.
What is a good conversion rate?
Although a high conversion rate is generally desirable, there is no guideline that can be used for evaluation. The level of a good conversion rate depends on the industry and varies from target to target. Seasonal fluctuations, the type of products on offer and many other factors can also have a strong influence on the percentage. In e-commerce, the conversion rate is usually between 1 and 5%, while in the media industry a guideline value of up to 10% is also common in some cases.
Influencing factors: What influences the conversion rate?The conversion rate is influenced by various internal and external factors. These include:
- Design of the website including placement of CTAs
- User-friendliness
- Website content
- Speed at which the website loads
- Credibility and awareness of the company
- Offer & price
- Needs of the target persons
- User behavior
- Market conditions & fluctuations
- Seasonality
The influencing factors vary depending on the type of website and the action to be tracked
Increasing the conversion rate: What is conversion rate optimization?
Conversion rate optimization (CRO) is the process that is used to optimize the conversion rate. The first step is to review the status quo. What are the conversion goals? What is the current conversion rate? In the next step, hypotheses are put forward as to why few conversions are being generated and what measures can be taken to increase the rate.
Why is optimization so important?
Conversion rates are used to measure the performance of websites and apps. The percentage shows the extent to which the goals that are of particular importance to a company are being achieved. If the percentage is too low, an increase in the rate can increase the number of clicks, downloads, sales, etc. with the same number of visitors. In this case, advertising expenditure can be reduced and still achieve the same performance as before. Alternatively, the additional revenue can be invested in new advertising campaigns. At the same time, an optimized conversion rate often has an effect on the ranking in search engines such as Google. By optimizing, you show Google that your website is valuable and relevant to users. Your ranking improves and often leads to an increase in organic traffic.
Which optimization methods?
Various measures can be taken to improve the conversion rate. The first step is to identify the reason for the low conversion rate. If your offer is unattractive and does not appeal to your target group, a low conversion rate is the logical consequence. However, if there is fundamental interest in your offer, the percentage can be increased simply by improving your website or your marketing activities.
Optimization of a landing page/shop
Even visual changes or textual adjustments can have a major impact on the conversion rate. These include, for example:
- Clearly worded headlines that contain value propositions
- Use of high-contrast colors
- Larger buttons that make clicking easier
- Placement of important page elements at the beginning of the page
- Use of meaningful calls to action
- Use of high-quality and appealing product images
- Integration of (info) graphics & videos
- Integration of a contact form, chat bots & co. to make it easier to get in touch
- Simple and secure ordering process
In addition, the functionality of the desktop and mobile versions of the landing page or the ordering process should always be kept in mind. A/B tests can be used to determine which changes achieve the desired success. These can be used to compare the performance of two versions and determine which version is more successful.
By continuously defining new conversion goals, identifying areas where the conversion rate can be improved and testing new features, the performance of the website or application can be continuously optimized.
Optimization of possible traffic generation sources
If a website operator has a low conversion rate as well as low traffic, optimizing traffic sources can push the conversion rate. Redesigning advertisements in the print area and/or for paid ads can already ensure that more potential customers land on the landing page and in turn have an impact on the conversion rate. Organic measures such as SEO also play a role here. The use of relevant keywords and treatment of important subject areas makes sense and ensures a better ranking in the search engine and increases the likelihood of an increase in traffic.
What does the conversion rate have to do with SEO?
The conversion rate is directly linked to SEO, as it is considered a ranking factor and therefore has a direct influence on the performance of a website. A high conversion rate can contribute to a website being classified as relevant by the search engine, such as Google, and being rewarded with a higher ranking. A higher ranking usually leads to an increase in organic traffic. Similarly, the metric can help to reduce the time spent on a website and the bounce rate. This can also have a positive impact on the ranking.
Conclusion: What is the conversion rate?
The conversion rate is a helpful indicator for measuring the success of your own website or advertising measures. Companies that sell their products or services online or at least have a digital presence in the form of a website want to draw the attention of interested parties to themselves and their offerings and sooner or later convert them into paying customers. A company therefore not only wants to generate traffic with targeted advertising measures and the website. As many of the website visitors as possible should carry out a transaction that the website operator is aiming for, a so-called conversion. This can range from filling out a form to the final purchase.
The conversion rate can be calculated using a simple formula and can reveal the need and potential for optimization. When exactly a conversion rate can be classified as good or bad depends on various influencing factors such as industry, user behavior of the target persons, seasonality, etc. There is no general statement or concrete guideline. In e-commerce, for example, a rate of 1 - 5 % can be used as a guide.
If the conversion rate is low, it can be optimized with various measures. Depending on the identified cause, the options can be divided into two areas: the optimization of traffic sources and the optimization of landing pages. Often, even small adjustments to the design, structure or content of a website to improve user-friendliness are enough to improve the percentage. Since the conversion rate is also very important in terms of SEO, it makes sense to track goals, check metrics and optimize the website and advertising measures.








