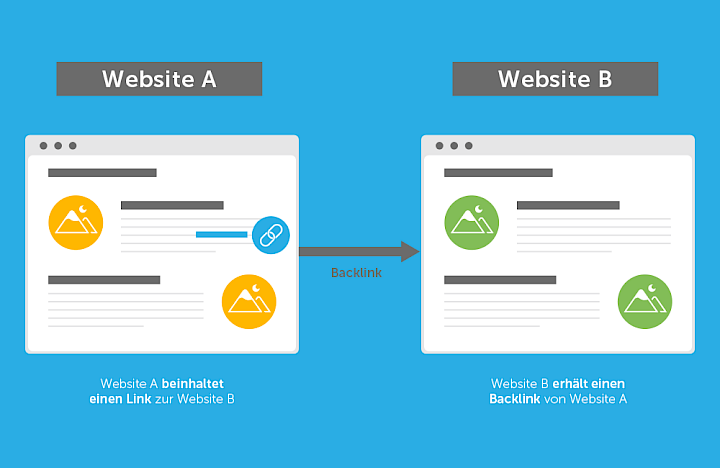
Backlink
Backlinks are hyperlinks that lead from one website/domain to another. At the beginning of the development of the internet, these links were used to navigate between different pages on the web. Over time, backlinks became important ranking factors for search engines. Today, the number of good backlinks, among other things, indicates the popularity of a website and is evaluated accordingly by Google and usually rewarded with a higher ranking or higher link popularity.
SEO: Why are backlinks so important for Google?
While on-page optimizations in the form of content, metadata, etc. also contribute significantly to the success of a website, these are ideally supported by off-page measures such as backlink building. These have an influence on the following areas:
Ranking
Google uses the number and quality of backlinks that lead to a specific domain as an indicator of its authority. A website with many, but high-quality, external links is classified as relevant and important by the algorithm and has a better chance of a higher ranking.
Referral traffic
Users who come to your site via external links provide you with additional traffic. This traffic is beneficial if it is links from pages with a certain value. The additional visitors you receive via the link are then potential customers and can ultimately have a positive effect on your turnover.
Indexing
Is your site new and not yet indexed? It can take some time for backlinks to show their effect. Pages that are already indexed but do not rank are also crawled less frequently by Google than popular pages in the top 3, as crawling is very resource-intensive for Google and therefore initially focuses on pages that are perceived as relevant. To speed up indexing in the future, Google has announced that it is testing IndexNow.
Google plans trial with IndexNow
Since October 2021, IndexNow has been offering website operators an interface with which website operators can independently report new pages and content to the search engine. The aim is to speed up indexing. IndexNow is currently only used by Bing and Yandex. Google announced in fall 2021 that it would launch a trial with IndexNow in 2022. No further information has yet been published.
The PageRank algorithm
Google uses the PageRank algorithm, among other things, to interpret the link data collected on the web. This was developed by Larry Page and Sergei Brin in 1996 and once formed the basis of Google's search algorithm. The more backlinks lead to a page, the higher the probability that a search engine crawler or a user will come across this page. Based on the linking structure, each website is assigned a PageRank and therefore a certain link popularity or link popularity. The basic principle: the higher the number of backlinks, the higher the PageRank or link popularity.
The sorting of search results for a keyword or phrase is now based on PageRank, among other things. Google wants to ensure that users are presented with the most relevant and important pages possible among the results for their search query.Will PageRank still be relevant in 2024?In 2017, the display of PageRank in the Google toolbar was deactivated. There is currently no copy of this publicly visible PageRank. As such, no taxative list is published of which factors are currently included in the evaluation of a link.However, it is known that high-quality backlinks from topic-relevant and/or trusted domains in particular have a positive influence on the ranking in search results. In addition, external links improve the findability of a website for the search engine algorithm.Backlinks after the Penguin updateA few years ago, the fact just described led to backlinks being distributed or deliberately built up in large numbers throughout the internet for search engine optimization. This was intended to trick the PageRank algorithm and even bad sites could achieve a good search engine ranking by buying lots of cheap links. Google's Penguin update in 2012 was intended to curb link spam. The newly developed algorithm specifically analyzed unnatural SEO attempts that did not comply with the guidelines. The ranking of affected pages in the search results deteriorated, and in some cases they were completely removed from the index.
The Penguin update mainly affected the following SEO measures:- Paid links
- Advertising link texts (money/brand anchor texts)
- An unnatural link growth
- Links from a non-topically relevant source
- Inferior backlinks from article directories, footers, blog comments, link networks, etc.
- Keyword stuffing
The relevance of internal and external links
The backlinks on a website can be divided into two groups. The URL can lead to a subpage of the current domain and can therefore be considered an internal link. External links, as the name suggests, lead to an external website.
Why are internal links important for SEO?Internal links within the domain, also known as deep links, help to distribute the link juice (also known as link power) more evenly across the individual subpages. When the Google bot arrives at a website, it follows the links according to the robots.txt file. This text file specifies which subpages the crawler should visit and index. It also makes it possible to exclude certain pages from indexing. The search engine bot analyzes the anchor texts of the individual links. It receives information about content correlations and determines the relevance to certain keywords.Usability also benefits from internal links. They help users with orientation and navigation through the website. Links refer to additional or further information and lead to the visitor staying on the page for longer. The length of stay is a user signal that can also have a positive effect on the ranking.Why are external links important for SEO?External links that lead to another domain as a text link, image link or via social signal or similar usually refer to sources or more in-depth information. This creates added value for the user and is included in the evaluation by the search engine crawlers. In particular, linked domains that are considered trustworthy and have a high domain trust are seen as a sign of quality. This usually includes Wikipedia on a regular basis. The search engine algorithm then assumes that relevant, high-quality information is provided on the linking website. This often also has an indirect positive effect on the ranking of the linking site.
Inbound links are backlinks that point from an external domain to your own website. In general, many inbound external links are a sign of the trustworthiness of a website. This is particularly the case if the backlinks come from a page with a high domain trust.The following applies: A high number of relevant inbound links from websites with a high level of trust has a positive effect on the ranking.
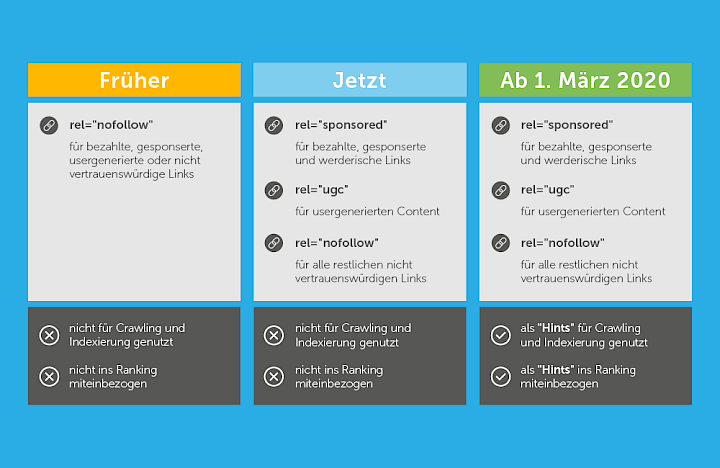
Dofollow, Nofollow, sponsored and UGC: What has changed compared to Dofollow/Nofollow
If different websites refer to each other via external links, the links in the source text are marked with a rel attribute. Rel stands for relationship. The designation helps search engine bots, browsers or other software to place the link in context.
If there is no rel attribute, a link is automatically classified as dofollow. This means that the search engine crawlers see the backlink as a recommendation of the referring website. The link is included in the ranking evaluation of the linked page.The evaluation of nofollow backlinksIf you want to place an external link on a website but mark it as untrustworthy, the link must be marked with rel="nofollow" in the source text. For a long time, this attribute caused the search engine bot to ignore the link and not follow it.
In September 2019, however, Google announced changes to this. From March 2020, nofollow links will be analyzed by the algorithms as "hints". This means that with "nofollow 2.0", such links can also have an influence on the rating of the page.Sponsored and UGC backlinks
As part of the changes to the nofollow attribute, Google also announced two new backlink labels. From now on, paid backlinks that serve as advertising, for example, must be marked with the sponsored attribute.
Links in content created by users (user-generated content) are to be marked with rel="ugc" in the source text. This gives website operators the opportunity to distance themselves from links created by users. This applies in particular to posts in forums or comments on blogs. It is not yet clear how these labels will influence the strength of a backlink or its rating. However, it can be assumed that they will also be included in the link rating.What do the new rel attributes mean for website operators?
Because the changes are backwards-compatible, existing backlinks do not necessarily have to be changed. Because Google crawlers will also follow nofollow links from March 2020, it is worth checking the entire link profile - e.g. with a good SEO agency.
How do backlinks work?
External links are stored in the HTML source code of a website. With https://www.dreikon.de/ as an example page, they are displayed as follows:
<a href="/en/" target="_self" title="Online Marketing Agency" rel="nofollow">Online Marketing</a>
<a ...> marks the beginning of the anchor element. The abbreviation href stands for hypertext-reference and refers to the URL where the document can be found.
The target instruction does not necessarily have to be present. It determines where the link is opened in the browser:
- target="_self" opens the URL in the current browser tab. This also happens if no target has been defined.
- target="_blank" causes the target page to be opened in a new tab or window.
The title attribute can optionally be used to display a text when the mouse cursor is moved over the link on the website.
The rel attribute (relationship) can mark a URL as a nofollow link. If a Google bot encounters a nofollow link, it will not follow it to the linked page. The content manager signals that the website does not want to be associated with the link target. This prevents linkjuice from being transmitted. This describes the strength and reputation of a link (PageRank).
If no rel attribute is set, the link is automatically considered a dofollow link. The Google bot follows the link and indexes it. This is considered a trust signal and has a positive effect on the ranking of the target page.
After the closed a tag, the anchor or anchor text is set. It can be clicked in the browser on the website as a link. In the example above, this is the term "Online Marketing". </a> closes the element.

Recognize and evaluate good and bad backlinks
In the early years of search engines, it was pretty simple: the more backlinks referred to a website, the higher its value and quality was considered to be. Accordingly, it was popular to trade in links to pages that met the requirements of the search engine bots but not the interests of the user.
Google is not the only one to have learned. The focus is now on the benefit of the content for the user. Today, numerous factors are important for the value and credibility of a backlink. The number of links to a page now only plays a minor role in the ranking.
Character traits of sources for "good" backlinks
- High-quality content: If a link comes from a website that is filled with high-quality, user-friendly content, the user signals will also be positive: Users will stay on the page for longer. This increases the likelihood that links will also be clicked on. Topic relevance: If the content or topic of the linking website is relevant to the target of the link, then it is a trustworthy source. If a backlink comes from a very generic page with a lot of general, superficial content, there is a risk of a negative impact on the ranking.Language, country of origin and top-level domain (TLD): With the exception of highly specific subject areas and international websites, backlinks have a higher relevance for the ranking if they originate from a domain in the same country with the same language.
- Authority at page level: A website that is widely known for a specific subject area and provides a lot of helpful content, data and expert tips has a high level of authority. Many people recommend it to others and send positive signals to Google. Traffic: If backlinks correspond to the content of the referring website and link to pages that provide further information, then they will also be clicked on by users. This is also a positive sign of relevance for the search engines.
What are bad backlinks?
In addition to the numerous positive signals that confirm the value of an external link, Google takes into account other factors with a negative effect on the ranking.
These characteristics can affect the value of a backlink:
- No accessibility of the linking website
- The referring domain is not indexed
- The referring domain contains low-quality content
- Keyword stuffing on the referring website
- Unnatural money anchor texts
- Exchanged and sometimes paid for
- Links from link networks
- Many links from one source
Evaluate backlinks using a link audit
Regularly checking the link profile of a website is worthwhile because backlinks are important ranking factors. Bad links can cause considerable damage to the ranking and should be devalued. Backlinks can be easily viewed using the Google Search Console. Under the menu item "Security and manual measures", you can see whether manual penalties have been imposed. An algorithmic penalty is a sanction automatically assigned by a Google algorithm. You will NOT find this type of penalty in the Search Console.
Link building and link removal (manual removal, disavow) etc.
Since backlinks are currently among the top 3 ranking factors alongside content and Google's RankBrain, consistent, sensible backlink purchasing and, if necessary, the removal of bad links brings clear advantages.
Especially if you want to make your own website better known or are just starting out, search engine optimizers should ensure the generation of high-quality backlinks in addition to on-page optimization. While the ranking used to depend heavily on the number of external links, today it is all about quality and a balanced link mix. Among other things, good links must come from trustworthy websites that Google considers to be reputable and relevant to the respective niche, but must not come exclusively from sites with a high PageRank.
If there are also far too many backlinks from websites with low authority and an unnatural link profile, your own site may be penalized. This was particularly evident after Google's Penguin updates. Even if links come from sites that are no longer accessible or are full of spam, this has negative consequences.
Link removal: how it works!
After carrying out a link audit, you have two options to reduce the number of bad backlinks:
- Contacting the webmaster of the link-providing website
- Devaluing the backlink with the Google Disavow tool
Removing links by contacting the webmaster of the linking website is very time-consuming. A request for deletion is often ignored due to the amount of work involved or a lack of interest.
In the Google Search Console, backlinks can be declared invalid using the disavow tool. The link remains on the source page but is ignored by the Google crawlers. Absolute caution is required when using this tool, as invalidating too many or the wrong links can lead to heavy losses in the ranking.
Caution: Before invalidation, a detailed audit of the links should be carried out to ensure that only inferior links are removed. Otherwise the ranking can be negatively affected.
Whether link removal makes sense must be decided on a case-by-case basis. However, it is important to note that any removal should also be accompanied by a build-up of high-quality backlinks. Deleting or devaluing external links will always weaken the link profile. In the long term, link building is effective.
Link building - what options are there for Google-compliant link building?
Google's quality guidelines for link exchange programs contain a long list of link building measures that can have a negative impact on the ranking of a website. In addition to purchased backlinks, this also includes the exchange or automated distribution of links. In addition, tools such as SEMRush or Ahrefs can help to view important metrics and the external links of the competition and take these into account when building your own backlink structure.
As an alternative, Google suggests creating a website that is as relevant to the topic as possible with high-quality, helpful content, with linkable assets that offer added value for users. In this way, visibility, awareness and external links are generated automatically. The higher the usefulness of the content, the higher the probability that other sites will link to a website.
Buying backlinks - is that dangerous?
If building valuable links is the goal, the question remains as to how best to obtain them. Ideally, links to your own website are created without any action on your part. Users link to the website because they want to make recommendations or make the content available to other users and share it. Normally, a page must first be made visible so that it can be found at all. Buying links is therefore often the obvious choice. But is this still appropriate or even dangerous?
The risks of buying backlinks
Google itself explicitly points out in its guidelines that buying or exchanging backlinks can have a negative impact on rankings (https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/66356?hl=de). There is a risk of a penalty. Backlinks with the sponsored or nofollow attribute are an exception. However, the value of such links for search engine optimization is low.
Links from UGC pages are usually easy to set up, but their value can be classified as very low.Backlinks from the content of a topic-relevant website with high authority and visibility, on the other hand, are among the particularly high-quality links. Here, however, you are dependent on the webmaster. The webmaster must enter the link "voluntarily"; if this is not the case, you would risk a Google penalty if there is no labeling.
It is often the case that links on sites specializing in link building, so-called link farms, are not marked as advertising and so you not only risk a penalty in the Google ranking, but also find yourself in a grey area in competition law.Buy backlinks: Yes or no?
When buying external links, you should always keep the risks in mind and weigh up whether such a link actually adds value to the website or the rankings and justifies the risk of a possible penalty. Google is constantly developing its algorithms for recognizing purchased backlinks, so even after months or years they can be recognized and influence the rankings.
In the end, every webmaster must decide for themselves whether they want to buy backlinks or rather focus their resources and budgets on creating high-quality (link-worthy) content.Conclusion: Backlinks are important
Backlinks are still one of the most important ranking factors for the evaluation of a website in 2024. In the past, they were used for orientation and navigation on the World Wide Web. Today, external links are even among the top 3 ranking factors. Currently, however, it has become more difficult to "prove" the quality of a website through links alone; Google also takes other factors much more into account in its evaluation.
Internal links are easier to set than external links. They refer to subpages within a domain and help to distribute the link power evenly. At the same time, they help with orientation and usability.
External links also create added value for the user, for example by referring to websites with further information. If you receive a backlink from a page with a high authority, this has a positive influence on the ranking.
However, not all external, inbound links have the same effect. Relevant backlinks come from websites with high-quality, topic-relevant content that have a high level of authority and visibility. It goes without saying that traffic and regular clicks are important.
A comprehensive link audit is worthwhile for the preparation and evaluation of search engine optimization by means of link building. Various tools are available for this purpose, which we would like to introduce to you as a small bonus.